转载请声明出处哦~,本篇文章发布于luozhiyun的博客:https://www.luozhiyun.com
本文使用的Istio源码是 release 1.5。
介绍
pilot-discovery是在Pilot中的核心服务,在Pilot中名为pilot-discovery,主要功能是从注册中心(如 kubernetes 或者 consul)获取信息并汇集,从 Kubernetes API Server 中获取流量规则,并将服务信息和流量规则转化为数据面可以理解的格式,通过标准的数据面 API 下发到网格中的各个SideCar中。
pilot-discovery包含了服务发现、配置规则发现、xDS配置下发。总体上打算分三篇来进行讲解,这一篇主要看看服务发现部分的实现。文章中有涉及xDS协议的一些东西,大家可以看看这篇文章:深入解读Service Mesh背后的技术细节。
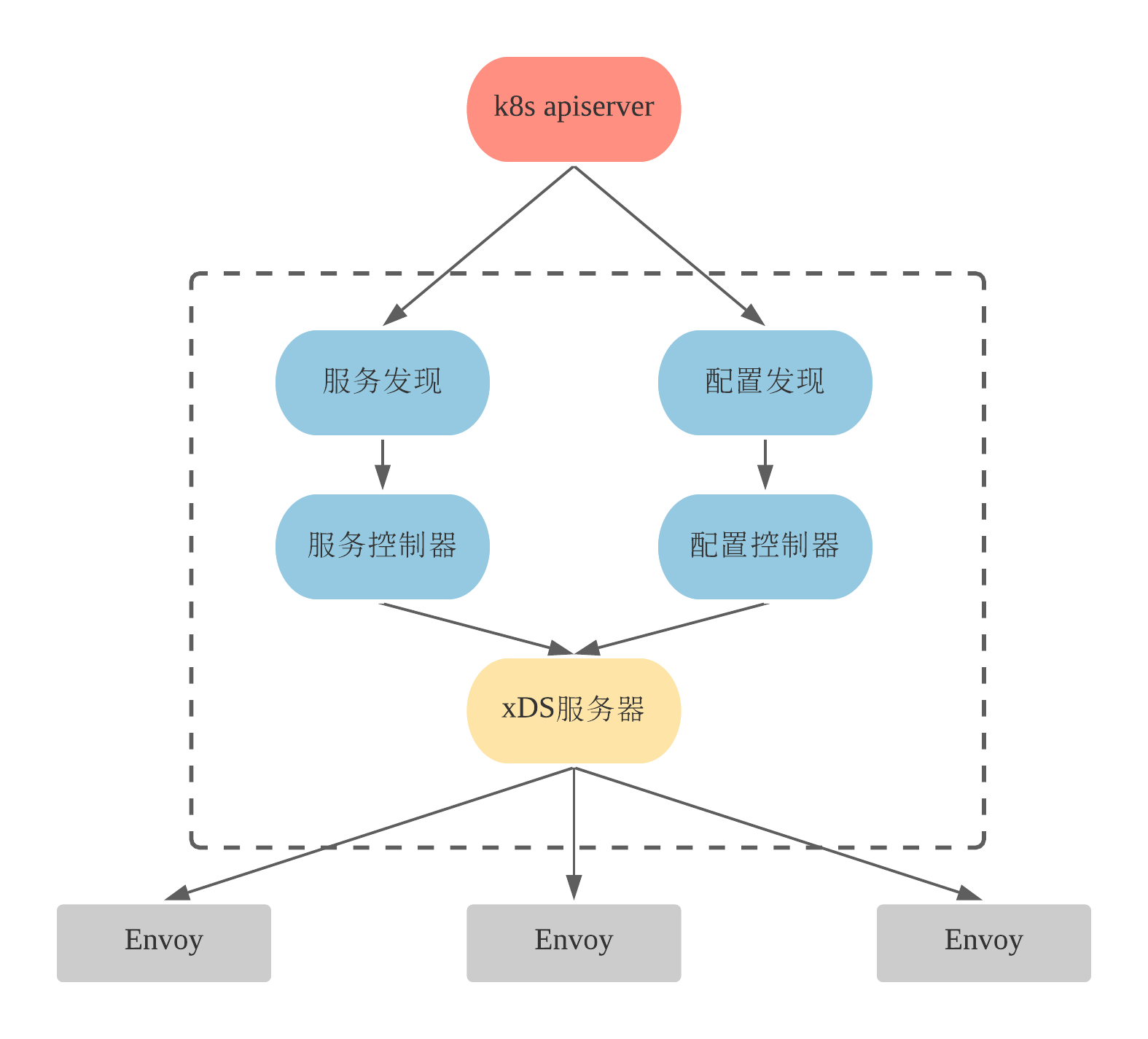
Pilot服务发现指通过监听底层平台的服务注册中心来缓存Istio服务模型,并且监视服务模型的变化,再服务模型更新时触发相关事件回调处理函数的执行。
服务发现工作机制
Pilot初始化
discoveryCmd = &cobra.Command{
Use: "discovery",
Short: "Start Istio proxy discovery service.",
Args: cobra.ExactArgs(0),
RunE: func(c *cobra.Command, args []string) error {
...
//日志配置
if err := log.Configure(loggingOptions); err != nil {
return err
}
...
stop := make(chan struct{})
// 创建xDs服务器
discoveryServer, err := bootstrap.NewServer(&serverArgs)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to create discovery service: %v", err)
}
// 启动服务器
if err := discoveryServer.Start(stop); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to start discovery service: %v", err)
}
//等待进程推出
cmd.WaitSignal(stop)
discoveryServer.WaitUntilCompletion()
return nil
},
}Pilot服务在初始化的时候首先会初始化日志配置,然后创建xDs服务器,这里的xDs指的是x Discovery Service的意思,x代表了一系列的组件如:Cluster、Endpoint、Listener、Route 等。
func NewServer(args *PilotArgs) (*Server, error) {
args.Default()
e := &model.Environment{
ServiceDiscovery: aggregate.NewController(),
PushContext: model.NewPushContext(),
}
s := &Server{
basePort: args.BasePort,
clusterID: getClusterID(args),
environment: e,
EnvoyXdsServer: envoyv2.NewDiscoveryServer(e, args.Plugins),
forceStop: args.ForceStop,
mux: http.NewServeMux(),
}
// 初始化处理Istio Config的控制器
if err := s.initConfigController(args); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("config controller: %v", err)
}
// 初始化处理Service Discovery的控制器
if err := s.initServiceControllers(args); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("service controllers: %v", err)
}
...
//初始化xDS服务端
if err := s.initDiscoveryService(args); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("discovery service: %v", err)
}
...
// Webhook 回调服务
if err := s.initHTTPSWebhookServer(args); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("injectionWebhook server: %v", err)
}
//sidecar注入相关
if err := s.initSidecarInjector(args); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("sidecar injector: %v", err)
}
...
return s, nil
}NewServer方法里面初始化了很多模块,这里挑相关的看看initConfigController是和配置服务相关的,我们之后再看,这里我们主要看initServiceControllers。
ServiceControllers
服务发现的主要逻辑在Pilot中由ServiceController(服务控制器)实现,通过监听底层平台的服务注册中心来缓存Istio服务模型,并监视服务模型的变化,在服务模型更新时触发相关事件回调处理函数的执行。
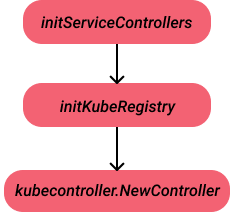
初始化
Controller的初始化执行流程很简单,这里用一张图来描述,initServiceControllers方法最后会调用到NewController方法来进行初始化。
func NewController(client kubernetes.Interface, options Options) *Controller {
log.Infof("Service controller watching namespace %q for services, endpoints, nodes and pods, refresh %s",
options.WatchedNamespace, options.ResyncPeriod)
// The queue requires a time duration for a retry delay after a handler error
// 初始化Controller
c := &Controller{
domainSuffix: options.DomainSuffix,
client: client,
//控制器任务队列
queue: queue.NewQueue(1 * time.Second),
clusterID: options.ClusterID,
xdsUpdater: options.XDSUpdater,
servicesMap: make(map[host.Name]*model.Service),
externalNameSvcInstanceMap: make(map[host.Name][]*model.ServiceInstance),
networksWatcher: options.NetworksWatcher,
metrics: options.Metrics,
}
//获取informer
sharedInformers := informers.NewSharedInformerFactoryWithOptions(client, options.ResyncPeriod, informers.WithNamespace(options.WatchedNamespace))
//注册 informer处理器
c.services = sharedInformers.Core().V1().Services().Informer()
//Services Handler
registerHandlers(c.services, c.queue, "Services", c.onServiceEvent)
//endpoints Handler
switch options.EndpointMode {
case EndpointsOnly:
c.endpoints = newEndpointsController(c, sharedInformers)
case EndpointSliceOnly:
c.endpoints = newEndpointSliceController(c, sharedInformers)
}
//Nodes Handler
c.nodes = sharedInformers.Core().V1().Nodes().Informer()
registerHandlers(c.nodes, c.queue, "Nodes", c.onNodeEvent)
podInformer := sharedInformers.Core().V1().Pods().Informer()
c.pods = newPodCache(podInformer, c)
//Pods Handler
registerHandlers(podInformer, c.queue, "Pods", c.pods.onEvent)
return c
}NewController方法里面首先是初始化Controller,然后获取informer后分别注册Services Handler、endpoints Handler、Nodes Handler、Pods Handler。
核心功能就是监听k8s相关资源(Service、Endpoint、Pod、Node)的更新事件,执行相应的事件处理回调函数。
这里的Controller结构体实现了Controller接口:
type Controller interface {
// AppendServiceHandler notifies about changes to the service catalog.
AppendServiceHandler(f func(*Service, Event)) error
// AppendInstanceHandler notifies about changes to the service instances
// for a service.
AppendInstanceHandler(f func(*ServiceInstance, Event)) error
// Run until a signal is received
Run(stop <-chan struct{})
}再注册完毕后会调用其Run方法异步执行。
//异步调用Run方法
go serviceControllers.Run(stop)
//run方法里面会遍历GetRegistries列表,并异步执行其Run方法
func (c *Controller) Run(stop <-chan struct{}) {
for _, r := range c.GetRegistries() {
go r.Run(stop)
}
<-stop
log.Info("Registry Aggregator terminated")
}到这里ServiceController为四种资源分别创建了一个监听器,用于监听K8s的资源更新,并注册EventHandler。
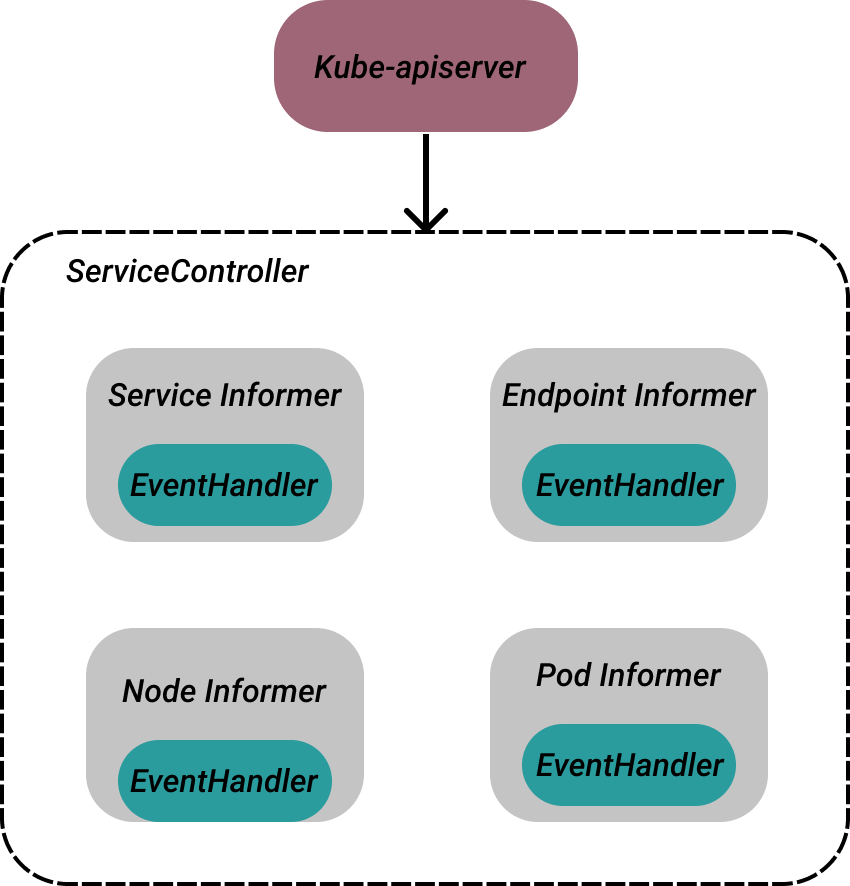
Service处理器
func (c *Controller) onServiceEvent(curr interface{}, event model.Event) error {
if err := c.checkReadyForEvents(); err != nil {
return err
}
svc, ok := curr.(*v1.Service)
if !ok {
tombstone, ok := curr.(cache.DeletedFinalStateUnknown)
if !ok {
log.Errorf("Couldn't get object from tombstone %#v", curr)
return nil
}
svc, ok = tombstone.Obj.(*v1.Service)
if !ok {
log.Errorf("Tombstone contained object that is not a service %#v", curr)
return nil
}
}
log.Debugf("Handle event %s for service %s in namespace %s", event, svc.Name, svc.Namespace)
//将k8s service 转换成 istio service
svcConv := kube.ConvertService(*svc, c.domainSuffix, c.clusterID)
//根据事件类型处理事件
switch event {
//删除事件
case model.EventDelete:
c.Lock()
delete(c.servicesMap, svcConv.Hostname)
delete(c.externalNameSvcInstanceMap, svcConv.Hostname)
c.Unlock()
// EDS needs to just know when service is deleted.
//更新服务缓存
c.xdsUpdater.SvcUpdate(c.clusterID, svc.Name, svc.Namespace, event)
default:
// instance conversion is only required when service is added/updated.
instances := kube.ExternalNameServiceInstances(*svc, svcConv)
c.Lock()
c.servicesMap[svcConv.Hostname] = svcConv
if instances == nil {
delete(c.externalNameSvcInstanceMap, svcConv.Hostname)
} else {
c.externalNameSvcInstanceMap[svcConv.Hostname] = instances
}
c.Unlock()
//更新服务缓存
c.xdsUpdater.SvcUpdate(c.clusterID, svc.Name, svc.Namespace, event)
}
// Notify service handlers.
// 触发XDS事件处理器
for _, f := range c.serviceHandlers {
f(svcConv, event)
}
return nil
}Service事件处理器会将根据事件的类型更新缓存,然后调用serviceHandlers的事件处理器进行回调。serviceHandlers事件处理器是在初始化DiscoveryService的时候设置的。
serviceHandler := func(svc *model.Service, _ model.Event) {
pushReq := &model.PushRequest{
Full: true,
NamespacesUpdated: map[string]struct{}{svc.Attributes.Namespace: {}},
ConfigTypesUpdated: map[resource.GroupVersionKind]struct{}{collections.IstioNetworkingV1Alpha3Serviceentries.Resource().GroupVersionKind(): {}},
Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.ServiceUpdate},
}
//配置更新
s.EnvoyXdsServer.ConfigUpdate(pushReq)
}Endpoint处理器
Endpoint处理器会在调用newEndpointsController创建endpointsController的时候进行注册
func newEndpointsController(c *Controller, sharedInformers informers.SharedInformerFactory) *endpointsController {
informer := sharedInformers.Core().V1().Endpoints().Informer()
out := &endpointsController{
kubeEndpoints: kubeEndpoints{
c: c,
informer: informer,
},
}
//注册处理器
out.registerEndpointsHandler()
return out
}在回调的时候会调用到endpointsController的onEvent方法:
func (e *endpointsController) onEvent(curr interface{}, event model.Event) error {
...
return e.handleEvent(ep.Name, ep.Namespace, event, curr, func(obj interface{}, event model.Event) {
ep := obj.(*v1.Endpoints)
//EDS更新处理
e.c.updateEDS(ep, event)
})
}这里会调用updateEDS进行EDS(Endpoint Discovery service)更新处理。
func (c *Controller) updateEDS(ep *v1.Endpoints, event model.Event) {
hostname := kube.ServiceHostname(ep.Name, ep.Namespace, c.domainSuffix)
endpoints := make([]*model.IstioEndpoint, 0)
if event != model.EventDelete {
for _, ss := range ep.Subsets {
for _, ea := range ss.Addresses {
//获取Endpoint对应的Pod实例
pod := c.pods.getPodByIP(ea.IP)
...
// 将Endpoint转换成Istio模型IstioEndpoint
for _, port := range ss.Ports {
endpoints = append(endpoints, &model.IstioEndpoint{
Address: ea.IP,
EndpointPort: uint32(port.Port),
ServicePortName: port.Name,
Labels: labelMap,
UID: uid,
ServiceAccount: sa,
Network: c.endpointNetwork(ea.IP),
Locality: locality,
Attributes: model.ServiceAttributes{Name: ep.Name, Namespace: ep.Namespace},
TLSMode: tlsMode,
})
}
}
}
}
//使用xdsUpdater更新EDS
_ = c.xdsUpdater.EDSUpdate(c.clusterID, string(hostname), ep.Namespace, endpoints)
}在这里会重新封装endpoints然后调用EDSUpdate进行更新。
func (s *DiscoveryServer) EDSUpdate(clusterID, serviceName string, namespace string,
istioEndpoints []*model.IstioEndpoint) error {
inboundEDSUpdates.Increment()
s.edsUpdate(clusterID, serviceName, namespace, istioEndpoints, false)
return nil
}
func (s *DiscoveryServer) edsUpdate(clusterID, serviceName string, namespace string,
istioEndpoints []*model.IstioEndpoint, internal bool) {
s.mutex.Lock()
defer s.mutex.Unlock()
requireFull := false
...
//找到之前缓存的服务
if _, f := s.EndpointShardsByService[serviceName]; !f {
s.EndpointShardsByService[serviceName] = map[string]*EndpointShards{}
}
ep, f := s.EndpointShardsByService[serviceName][namespace]
//不存在则初始化
if !f {
ep = &EndpointShards{
Shards: map[string][]*model.IstioEndpoint{},
ServiceAccounts: map[string]bool{},
}
s.EndpointShardsByService[serviceName][namespace] = ep
if !internal {
adsLog.Infof("Full push, new service %s", serviceName)
requireFull = true
}
}
...
ep.mutex.Lock()
ep.Shards[clusterID] = istioEndpoints
ep.ServiceAccounts = serviceAccounts
ep.mutex.Unlock()
if !internal {
var edsUpdates map[string]struct{}
if !requireFull {
edsUpdates = map[string]struct{}{serviceName: {}}
}
//配置更新
s.ConfigUpdate(&model.PushRequest{
Full: requireFull,
NamespacesUpdated: map[string]struct{}{namespace: {}},
ConfigTypesUpdated: map[resource.GroupVersionKind]struct{}{collections.IstioNetworkingV1Alpha3Serviceentries.Resource().GroupVersionKind(): {}},
EdsUpdates: edsUpdates,
Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.EndpointUpdate},
})
}
}edsUpdate方法里面实际上就是做了两件事,一是更新缓存,二是调用ConfigUpdate进行配置更新。
ConfigUpdate资源更新实际上就是通过事件分发执行xDS分发,这块的细节我们稍后再讲。
总结
通过这篇我们掌握了服务发现是通过k8s的Informer来注册监听Service、EndPoint、nodes、pods等资源的更新事件,然后通过事件驱动模型执行回调函数,再调用xDS的ConfigUpdate来执行异步更新配置的操作。
Reference
https://www.servicemesher.com/blog/istio-analysis-4/
https://www.cnblogs.com/163yun/p/8962278.html
https://www.servicemesher.com/blog/envoy-proxy-config-deep-dive/